Spectrum Representation
- The spectrum is a compact representation of the frequency content of a signal composed of sinusoids.
$x(t)=Acos(2\pi f_{0}t+\varphi )=\Re \left\{Xe^{j2\pi f_{0}t} \right\}$
- Where $Ae^{j\varphi }=X$ is a phasor, and we recognized how phasor couldbe simply the additionof the same frequency.
-
The complicated waveform is constructed from sums of sinusoidal signals of different amplitudes, phases, and frequencies.
-
The spectrum is simply the collection of the amplitude, phase, and frequency information that allows us to express the signal as

스펙트럼은 사인파로 구성된 신호의 주파수 내용을 간결하게 표현한 것임.
여기서 우리는 $Ae^{j\varphi}=X$가 위상이며, 위상이 단순히 같은 주파수의 가산임을 인식했음.
복잡한 파형은 서로 다른 진폭, 위상 및 주파수의 사인파 신호의 합으로 구성됨.
스펙트럼은 단순히 진폭, 위상, 주파수 정보의 집합으로 신호를 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있음.
The spectrum of a Sum of Sinusoids
- $x(t)=A_{0}+\sum_{k=1}^{N}A_{k}cos(2\pi f_{k}t+\varphi _{k})$
- The new signal from sinusoids is the additive linear combination
- where a signal is obtained by summation together a constant and N sinusoids, each with a different frequency, amplitude, and phase
사인파의 새로운 신호는 추가 선형 결합임.
여기서 신호는 각각 다른 주파수, 진폭 및 위상을 가진 상수와 N개의 사인파를 합하여 얻어짐.
Euler's Formula Reversed
- Solve for cosine (or sine)
$\\e^{j\omega t}=cos(\omega t)+jsin(\omega t)\\e^{-j\omega t}=cos(-\omega t)+jsin(-\omega t)\\e^{-j\omega t}=cos(\omega t)-jsin(\omega t)\\e^{j\omega t}+e^{-j\omega t}=2cos(\omega t)$
$cos(\omega t)=\frac{1}{2}(e^{j\omega t}+e^{-j\omega t})$
INVERSE Euler's Formula
- Solve for cosine( or sine)
$\\ cos(\omega t)=\frac{1}{2}(e^{j\omega t}+e^{-j\omega t})\\sin(\omega t)=\frac{1}{2j}(e^{j\omega t}-e^{-j\omega t})$
- $x(t)=X_{0}+\sum_{N}^{k=1}\left\{\frac{X_{k}}{2}e^{j2\pi f_{k}t}+\frac{X_{k}}{2}e^{-j2\pi f_{k}t} \right\}$
- The real part of a complex number is equal to one-half the sum of that number and its complex conjugate
- Above eq. shows that each sinusoid in the sum decomposed into two rotating phasors, one with positive frequency, and the other with negative frequency.
복소수의 실수 부분은 그 수와 복소수 공역의 합의 1/2과 같음.
위의 eq는 합의 각 사인파가 2개의 회전 위상으로 분해되어 하나는 양 주파수이고 다른 하나는 음의 주파수임을 나타냄.
Two-sided spectrum
- $\left\{(0,X_{0}),\;(f_{1},\frac{1}{2}X_{1}),\;(-f_{1},\frac{1}{2}X_{1}),\;...\; (f_{k},\frac{1}{2}X_{k}),\;(-f_{k},\frac{1}{2}X_{k}),... \right\}$
- Each pair $(f_{k},\frac{1}{2}X_{k})$ indicates the size and relative phase of the sinusoidal component contributing at frequency $f_{k}$
-
It is common to refer to the spectrum as the frequency-domain representation
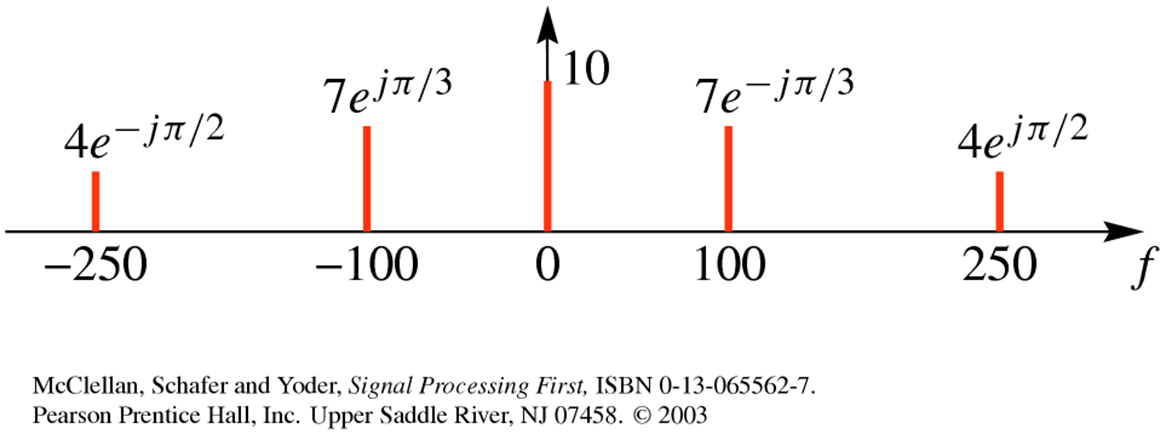
- $x(t)=10+14cos(200\pi t-\pi/3)+8cos(500\pi t-\pi/2)$
- $\\x(t)=10+7e^{-j\frac{\pi}{3}}e^{j2\pi(100)t}+7e^{j\frac{\pi}{3}}e^{j2\pi(250)t}+4e^{-j\frac{\pi}{2}}e^{-j2\pi(250)t}$
$\left\{(0,10),\;(100,7e^{-j\frac{\pi}{3}}),\;(-100,7e^{j\frac{\pi}{3}}),\; (250,4e^{j\frac{\pi}{3}}),\; (-250,4e^{-j\frac{\pi}{2}}) \right\}$
각 쌍 $(f_{k},\frac{1}{2}X_{k})$는 주파수 $f_{k}$에서 기여하는 사인파 성분의 크기와 상대 위상을 나타냄.
주파수 영역 표현으로서 스펙트럼을 참조하는 것이 일반적임.
FREQUENCY DIAGRAM
- Plot Complex Amplitude vs. Freq
- $x(t)=10+14cos(200\pi t-\pi/3)+8cos(500\pi t-\pi/2)$





댓글