컬렉션
컬렉션 (Collection)
- 같은 성격을 띈 데이터의 모음을 담는 자료구조
- 배열(System.Array 클래스)도 .NET 이 제공하는 다양한 컬렉션 자료구조의 일부
- ICollection 인터페이스를 상속

- .NET 이 제공하는 주요 컬렉션 자료구조
- ArrayList
- Queue
- Stack
- Hashtable
ArrayList
ArrayList
배열과 같이 인덱스를 이용하여 요소에 접근 가능. 필요에 따라 동적으로 크기가 증가.
- 가장 배열과 닮은 컬렉션
- 컬렉션의 요소에 접근할 때는 [ ] 연산자 이용
- 특정 위치에 있는 요소에 데이터를 임의로 할당 가능
- 배열과 달리 필요에 따라 자동으로 용량이 늘어나거나 줄어듦 (용량을 미리 지정할 필요 없음)
- ArrayList 의 주요 메소드
- Add() : 가장 마지막에 있는 요소 뒤에 새 요소를 추가
- RemoveAt() : 특정 인덱스에 있는 요소를 제거
- Insert() : 원하는 위치에 새요소를 삽입
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.Add(10);
list.Add(20);
list.Add(30);
list.RemoveAt(1); // 20을 삭제
list.Insert(1, 25); // 25를 1번 인덱스에 삽입, 즉, 10과 30 사이에 25를 삽입
list[0] = 11;
Console.WriteLine(list[0]); //11 출력
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace UsingList
{
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
list.Add(i);
foreach (object obj in list)
Console.Write($"{obj} ");
Console.WriteLine();
list.RemoveAt(2);
foreach (object obj in list)
Console.Write($"{obj} ");
Console.WriteLine();
list.Insert(2, 2); //2번 인덱스에 2 삽입
foreach (object obj in list)
Console.Write($"{obj} ");
Console.WriteLine();
list.Add("abc");
list.Add("def");
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
Console.Write($"{list[i]} ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
ArrayList : 다양한 형식의 객체를 입력
- ArrayList 는 다양한 형식의 객체를 담을 수 있음
- Add( ), Insert( ) 메소드는 object 형식의 매개변수 사용
- 모든 데이터 형식을 object 형식의 매개변수로 입력 받는 것이 가능
public virtual int Add(object? value);
public virtual void Insert(int index, object? value);- object 데이터 형식은 값 형식의 데이터를 처리하기 위해 박싱, 언박싱 수행
- 박싱, 언박싱은 적지 않은 오버헤드를 요구하는 작업
- C# 은 오버헤드를 줄이기 위해 일반화 컬렉션 제공
Queue
Queue
데이터를 차례대로 넣고 입력한 순서로 하나씩 처리 : CPU의 작업, 프린터의 여러 문서 출력, 스트리밍 서비스에서 콘텐츠 버퍼링
- Queue 는 대기열, 즉 기다리는(대기) 줄(열)이라는 뜻
- 입력은 오직 뒤에서, 출력은 앞에서만 이루어짐
- Queue 방식의 활용
- OS에서 CPU가 처리해야 할 작업을 정리할 때
- 프린터가 여러 문서를 처리할 때
- Queue 의 주요 메소드
- Enqueue() : 가장 마지막에 있는 항목 뒤에 새 항목을 추가
- Dequeue() : 제일 앞에 있던 항목이 출력
Queue que = new Queue();
que.Enqueue(1);
que.Enqueue(2);
int a = (int)que.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine(a); // 출력 값: 1
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace UsingQueue
{
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
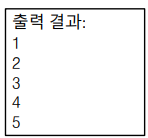
Queue que = new Queue();
que.Enqueue(1);
que.Enqueue(2);
que.Enqueue(3);
que.Enqueue(4);
que.Enqueue(5);
while (que.Count > 0)
Console.WriteLine(que.Dequeue());
}
}
}
Stack
Stack
- Queue 와 반대로 먼저 들어온 데이터가 나중에 출력 (First In – Last Out)
- 나중에 들어온 데이터는 먼저 출력 (Last In – First Out)
- Stack 의 주요 메소드
- Push() : 데이터를 넣을 때, 데이터를 위에 쌓음
- Pop() : 제일 위에 쌓여 있는 데이터를 꺼냄
- Pop()을 호출하여 데이터를 꺼내면, 그 데이터는 컬렉션에서 제거
- 그 아래 있던 데이터가 가장 위로 올라옴
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.Push(1); // 최상위 데이터는 1
stack.Push(2); // 최상위 데이터는 2
stack.Push(3); // 최상위 데이터는 3
int a = (int)stack.Pop(); // 최상위 데이터는 다시 2
Console.WriteLine(a); // 출력값: 3
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace UsingStack
{
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.Push(1); // 최상위 데이터는 1
stack.Push(2); // 최상위 데이터는 2
stack.Push(3); // 최상위 데이터는 3
stack.Push(4); // 최상위 데이터는 4
stack.Push(5); // 최상위 데이터는 5
while (stack.Count > 0)
Console.WriteLine(stack.Pop());
}
}
}
Hashtable
Hashtable
- 키(key)와 값(value)의 쌍으로 이루어진 데이터를 다룰 때 사용
- 영어사전을 예로 들어, “book”을 키로, “책”을 값으로 입력
- 탐색속도가 빠르고 사용하기 편리함
- 해싱 (Hashing)
- 원하는 데이터를 찾을 때, 키를 이용해 단번에 데이터가 저장된 컬렉션 내 주소 계산
- 어떤 형식이든 키로 사용할 수 있음 (예: int, float, string)
- 배열에서 인덱스를 이용해 배열요소에 접근하는 것에 준하는 탐색속도를 가짐
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
ht["book"] = "책";
ht["cook"] = "요리사";
ht["tweet"] = "지저귀다";
Console.WriteLine(ht["book"]); // 출력값: 책
Console.WriteLine(ht["cook"]); // 출력값: 요리사
Console.WriteLine(ht["tweet"]); // 출력값: 지저귀다배열과 비교한 장점 : 데이터를 저장할 요소의 위치로 키 사용, 키로 사용할 수 있는 데이터 형식에 제한이 없음.
키를 해싱해서 테이블 내의 주소를 계산
배열처럼 다루기 간편하고 탐색속도도 빠름.
using System;
using System.Collections;
using static System.Console;
namespace UsingHashtable
{
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
ht["하나"] = "one";
ht["둘"] = "two";
ht["셋"] = "three";
ht["넷"] = "four";
ht["다섯"] = "five";
WriteLine( ht["하나"] ) ;
WriteLine( ht["둘"] );
WriteLine( ht["셋"] );
WriteLine( ht["넷"] );
WriteLine( ht["다섯"] );
}
}
}
컬렉션 초기화
컬렉션 초기화
- ArrayList, Queue, Stack은 배열을 이용해 초기화 가능
- 컬렉션 생성자를 호출할 때 배열의 객체를 매개변수로 입력
- 컬렉션 객체는 해당 배열을 바탕으로 내부 데이터를 채움
/*배열을 통한 초기화*/
int[] arr = { 123, 456, 789 };
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(arr); // 123, 456, 789
Stack stack = new Stack(arr); // 789, 456, 123
Queue queue = new Queue(arr); // 123, 456, 789- ArrayList 는 컬렉션 초기자를 이용해 초기화 가능
- 컬렉션 초기자는 생성자를 호출할 때, 생성자 뒤에 { 와 } 사이에 컬렉션 요소의 목록을 입력하여 사용
/*배열의 도움 없이 직접 컬렉션 초기자로 초기화*/
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList() { 11, 22, 33 };- 딕셔너리 초기자를 이용한 초기화
- Hashtable
Hashtable 초기화
- Hashtable 초기화를 위해 딕셔너리 초기자(Dictionary Initializer) 이용
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable()
{
["하나"] = 1, // ;가 아니라 ,를 이용하여 항목을 구분함
["둘"] = 2,
["셋"] = 3
};- Hashtable 초기화를 위해 컬렉션 초기자도 이용 가능
Hashtable ht2 = new Hashtable()
{
{ "하나",1},
{ "둘",2},
{ "셋",3}
};
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace InitializingCollections
{
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
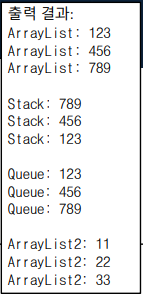
int[] arr = { 123, 456, 789 };
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(arr);
foreach (object item in list)
Console.WriteLine($"ArrayList : {item}");
Console.WriteLine();
Stack stack = new Stack(arr);
foreach (object item in stack)
Console.WriteLine($"Stack : {item}");
Console.WriteLine();
Queue queue = new Queue(arr);
foreach (object item in queue)
Console.WriteLine($"Queue : {item}");
Console.WriteLine();
//컬렉션 초기자 사용
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList() { 11, 22, 33 };
foreach (object item in list2)
Console.WriteLine($"ArrayList2 : {item}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
'전공 > C# 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 11강. 인터페이스와 추상 클래스 (1) (0) | 2023.05.23 |
|---|---|
| 10강. 인덱서 (Indexer) & foreach가 가능한 객체 만들기 (0) | 2023.04.20 |
| 8강. 배열 (2) (0) | 2023.04.19 |
| 8강. 배열 (1) (0) | 2023.04.19 |
| 7강. 객체지향 프로그래밍과 클래스 (6)튜플 (0) | 2023.04.19 |




댓글