클래스 간의 형식 변환
클래스 간의 형식 변환
- 타입을 정의하는 것은 “단위 (unit)”를 사용하는 프로그램에 유용
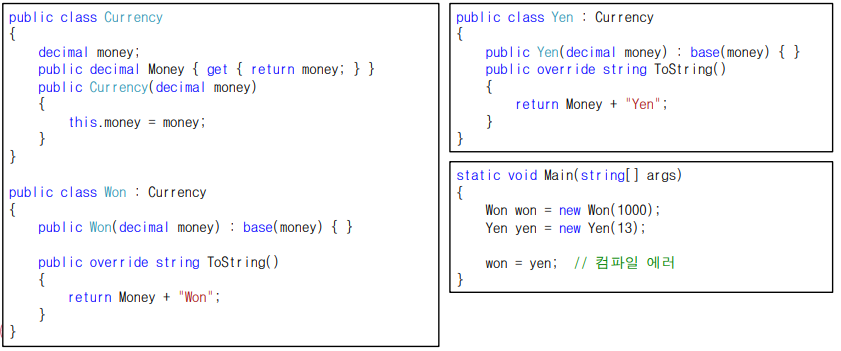
- 예를 들어, 원, 달러, 엔화와 같은 통화 (currency) 단위 사용의 경우
- 모든 종류의 통화를 하나의 타입으로 지정하면 금전 계산에 오류 발생의 여지 있음
- 아래 코드에서 달러를 엔화에 그대로 대입하면 계산의 오류 발생

- 원화와 엔화에 대한 클래스 정의
- 서로 다른 클래스의 객체를 바로 대입할 수 없음
클래스 간의 형식 변환 : implicit 연산자
- 서로 다른 클래스의 객체 사이의 형식 변환 가능
- 즉, 두 객체 사이의 대입 연산자 (=) 사용 가능
- 암시적, 명시적 형식 변환 모두 가능
- 통화 (currency) 예에서 환율을 적용한 계산 가능
using System;
namespace TypeConversion
{
public class Currency
{
decimal money;
public decimal Money { get { return money; } }
public Currency(decimal money)
{
this.money = money;
}
}
public class Won : Currency
{
public Won(decimal money) : base(money) { }
public override string ToString()
{
return Money + "Won";
}
}
public class Yen : Currency
{
public Yen(decimal money) : base(money) { }
public override string ToString()
{
return Money + "Yen";
}
static public implicit operator Won(Yen yen)
{
return new Won(yen.Money * 13m);
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Yen yen = new Yen(100);
Won won1 = yen; // 암시적(implicit) 형변환
Won won2 = (Won)yen;// 명시적(explicit) 형변환
Console.WriteLine(won1 + ", " + won2);
}
}
}
클래스 간의 형식 변환 : explicit 연산자
- explicit 연산자를 사용해 명시적 형식 변환만 가능하도록 설정 가능
using System;
namespace TypeConversion
{
public class Currency
{
decimal money;
public decimal Money { get { return money; } }
public Currency(decimal money)
{
this.money = money;
}
}
public class Won : Currency
{
public Won(decimal money) : base(money) { }
public override string ToString()
{
return Money + "Won";
}
}
public class Dollar : Currency
{
public Dollar(decimal money) : base(money) { }
public override string ToString()
{
return Money + "Dollar";
}
static public explicit operator Won(Dollar dollar)
{
return new Won(dollar.Money * 1000m);
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dollar dollar = new Dollar(1);
//Won won3 = dollar; // 암시적 형변환 불가능 (에러발생)
Won won4 = (Won)dollar; // 명시적 형변환
Console.WriteLine(won4);// 출력 1000Won
}
}
}클래스의 읽기 전용
읽기 전용 필드
- readonly 키워드를 사용하여 정의하는 읽기 전용 필드
- 생성자에서 초기화 가능
- 초기화 후에는 중간에 값 변경 불가
- 생성자 외 다른 메소드에서 값 변경 시 컴파일 에러 발생

using System;
namespace ReadonlyFields
{
class Configuration
{
readonly int min;
readonly int max;
public Configuration(int v1, int v2)
{
min = v1;
min = v2;
}
public void ChangeMax(int newMax)
{
//max = newMax; //컴파일 에러
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Configuration c = new Configuration(100, 10);
}
}
}읽기 전용 메소드
- readonly 키워드 사용하여 메소드 선언
- 구조체에서만 선언 가능 (구조체에 대해서는 밑에서 더 설명)
- 읽기 전용 메소드에서 구조체의 필드를 바꾸려 하면 컴파일 에러 발생

using System;
namespace ReadonlyMothod
{
struct ACSetting
{
public double currentInCelsius; // 현재 온도(°C)
public double target; // 희망 온도
public readonly double GetFahrenheit()
{
//target = currentInCelsius * 1.8 + 32; 컴파일 에러, 화씨(°F) 계산 결과를 target에 저장
return target; // target 반환
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ACSetting acs;
acs.currentInCelsius = 25;
acs.target = 25;
Console.WriteLine($"{acs.GetFahrenheit()}");
Console.WriteLine($"{acs.target}");
}
}
}중첩 클래스
중첩 클래스
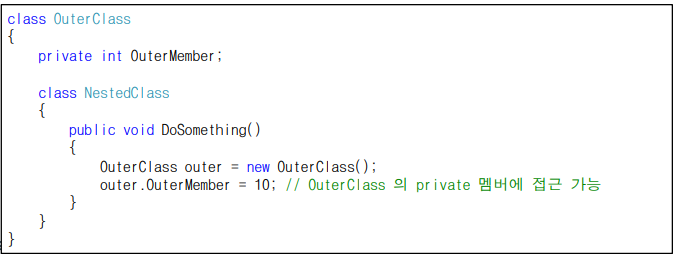
- 클래스 안에 클래스 선언
- 객체를 생성하고 메소드를 호출하는 방법은 일반 클래스 다르지 않음
- 일반 클래스와 차이점은 자신이 소속된 클래스의 멤버에 자유롭게 접근
- 자신이 소속된 클래스의 private 멤버에도 접근 가능
클래스 안에 선언되어 있는 클래스 : 소속되어 있는 클래스의 멤버에 자유롭게 접근 (private 멤버 포함)
사용 이유 : 클래스 외부에 공개하고 싶지 않은 형식을 만들고자 할 때, 현재 클래스의 일부처럼 표현 가능한 클래스를 만들고자 할 때
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace NestedClass
{
class Configuration
{
// List 는 앞으로 배울 새로운 자료구조
List<ItemValue> listConfig = new List<ItemValue>();
public void SetConfig(string item, string value)
{
ItemValue iv = new ItemValue();
iv.SetValue(this, item, value);
}
public string GetConfig(string item)
{
foreach (ItemValue iv in listConfig)
{
if (iv.GetItem() == item)
return iv.GetValue();
}
return "";
}
private class ItemValue // 외부에서 접근 불가
{
private string item;
private string value;
public void SetValue(Configuration config, string item, string value)
{
this.item = item;
this.value = value;
bool found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < config.listConfig.Count; i++)
{
if (config.listConfig[i].item == item)
{
config.listConfig[i] = this;
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (found == false)
config.listConfig.Add(this);
}
public string GetItem()
{ return item; }
public string GetValue()
{ return value; }
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.SetConfig("Version", "V 5.0");
config.SetConfig("Size", "655,324 KB");
Console.WriteLine(config.GetConfig("Version"));
Console.WriteLine(config.GetConfig("Size"));
config.SetConfig("Version", "V 5.0.1");
Console.WriteLine(config.GetConfig("Version"));
}
}
}
분할 클래스
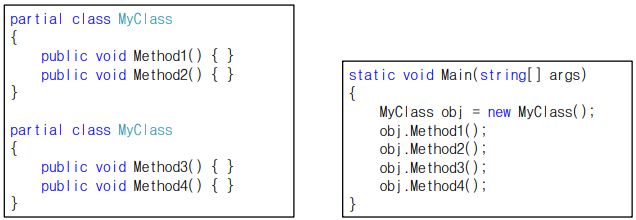
분할 클래스
- 여러 번에 나눠서 구현하는 클래스
- partial 키워드를 이용
- 클래스의 구현이 길어질 경우 여러 파일에 나눠서 구현 → 소스 코드 관리의 편의를 제공
- 컴파일러는 하나의 클래스로 묶어서 컴파일
using System;
namespace PartialClass
{
partial class MyClass
{
public void Method1()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1");
}
public void Method2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2");
}
}
partial class MyClass
{
public void Method3()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method3");
}
public void Method4()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method4");
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
obj.Method1();
obj.Method2();
obj.Method3();
obj.Method4();
}
}
}확장 메소드
확장 메소드
- 기존 클래스의 기능을 확장하는 기법
- 예를 들어, string 클래스에 문자열을 뒤집는 기능을 넣을 수 있음
- 또한 int 형식에 제곱 연산 기능을 넣을 수도 있음

using System;
using MyExtension;
namespace MyExtension
{
public static class IntegerExtension
{
public static int Square(this int myInt)
{
return myInt * myInt;
}
public static int Power(this int myInt, int exponent)
{
int result = myInt;
for (int i = 1; i < exponent; i++)
result = result * myInt;
return result;
}
}
}
namespace ExtensionMethod
{
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{3}^2 : {3.Square()}");
Console.WriteLine($"{3}^{4} : {3.Power(4)}");
Console.WriteLine($"{2}^{10} : {2.Power(10)}");
}
}
}
구조체
구조체
- struct 키워드를 사용하고 클래스와 상당 부분 비슷함
- 필드와 메소드를 가짐
클래스 : 참조 형식, 구조체 : 값 형식 / 클래스 인스턴스 : 가비지 콜렉터가 제거, 구조체 인스턴스 : 스택이 자동 제거
using System;
namespace Structure
{
struct Point3D
{
public int X;
public int Y;
public int Z;
public Point3D(int X, int Y, int Z)
{
this.X = X;
this.Y = Y;
this.Z = Z;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format($"{X}, {Y}, {Z}");
}
}
class MainApp
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point3D p3d1;
p3d1.X = 10;
p3d1.Y = 20;
p3d1.Z = 40;
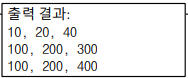
Console.WriteLine(p3d1.ToString());
Point3D p3d2 = new Point3D(100, 200, 300);
Point3D p3d3 = p3d2;
p3d3.Z = 400;
Console.WriteLine(p3d2.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(p3d3.ToString());
}
}
}
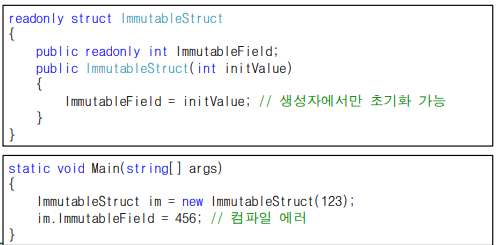
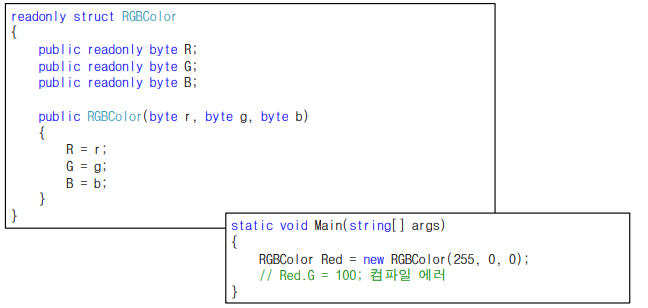
변경 불가능 구조체 선언
- readonly 키워드 사용하여 구조체 선언
- 모든 필드와 프로퍼티 값을 수정 할 수 없음
- 해당 구조체의 모든 필드가 readonly 로 선언되도록 강제
'전공 > C# 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 8강. 배열 (1) (0) | 2023.04.19 |
|---|---|
| 7강. 객체지향 프로그래밍과 클래스 (6)튜플 (0) | 2023.04.19 |
| 7강. 객체지향 프로그래밍과 클래스 (4)다형성 (0) | 2023.04.18 |
| 7강. 객체지향 프로그래밍과 클래스 (3)상속성 (0) | 2023.04.17 |
| 7강. 객체지향 프로그래밍과 클래스 (2)은닉성(캡슐화) (0) | 2023.04.17 |




댓글